The integration of LLMs into spreadsheets is transforming how people work in Excel. Two tools are currently leading this shift: GPT for Excel, a truly integrated add-in that brings bulk LLM processing directly into your workbook, and Microsoft Copilot’s native Excel integration, which focuses on data visualization and guided assistance.
While both tools use similar interfaces, they are built to solve very different tasks. GPT for Excel handles bulk LLM operations directly inside the spreadsheet, allowing you to translate thousands of rows, generate content in bulk, categorize, score, and triage a big batch of leads or customer feedback, run large-scale web research, and extract information from images in bulk. Copilot, on the other hand, specializes in visual and UI-driven actions such as generating pivot tables, charts, and formatting. However, its outputs often appear as previews or downloadable CSV files, requiring the user to copy and paste results back into the workbook, which can interrupt the natural Excel workflow.
TL;DR
- GPT for Excel is built for bulk operations, reliably completing hundreds or thousands of tasks directly in the sheet. Copilot currently encounters limitations on larger workloads.
- Copilot is designed for interactive assistance, guided analysis, and data visualization, but not large-scale automation.
- GPT for Excel uses pay-as-you-go pricing, offers full model choice, and executes tasks directly inside Excel, making it far more scalable than Copilot’s fixed per user subscription model which is heavily limited in volume and speed.
Quick comparison: GPT for Excel vs. Copilot in Excel
Feature | GPT for Excel | Copilot in Excel |
|---|---|---|
Primary use case | Bulk automation, large-scale LLM operations | Guided assistance, summaries, charts, formatting |
Bulk processing | Handles up to 1 million rows in one run | Stalls, refuses, or outputs incomplete results on large tasks |
Output handling | Inserts full results directly into cells | Produces previews or CSV downloads |
Progress tracking | Built-in live progress tracker | No progress visibility during execution |
Web search | Yes, live web lookups via Perplexity & Gemini with search grounding | No live internet access; relies on pretrained knowledge |
Image analysis | Yes, bulk extraction directly into cells | No image processing support |
Model choice | Multiple providers (GPT, Claude, Gemini, etc.) | No model selection; hidden model |
Speed | Up to 900 rows/minute | Up to 9 rows/minute |
Reliability | High, consistent at scale | Low, function ceilings, N/A values, preview-only outputs |
Pricing | Pay-as-you-go; no usage caps | ~$360/year per user |
Best for | High-volume workflows, bulk research, enrichment | Beginners needing quick summaries or visualizations |
Bulk processing works with GPT for Excel, not with Copilot
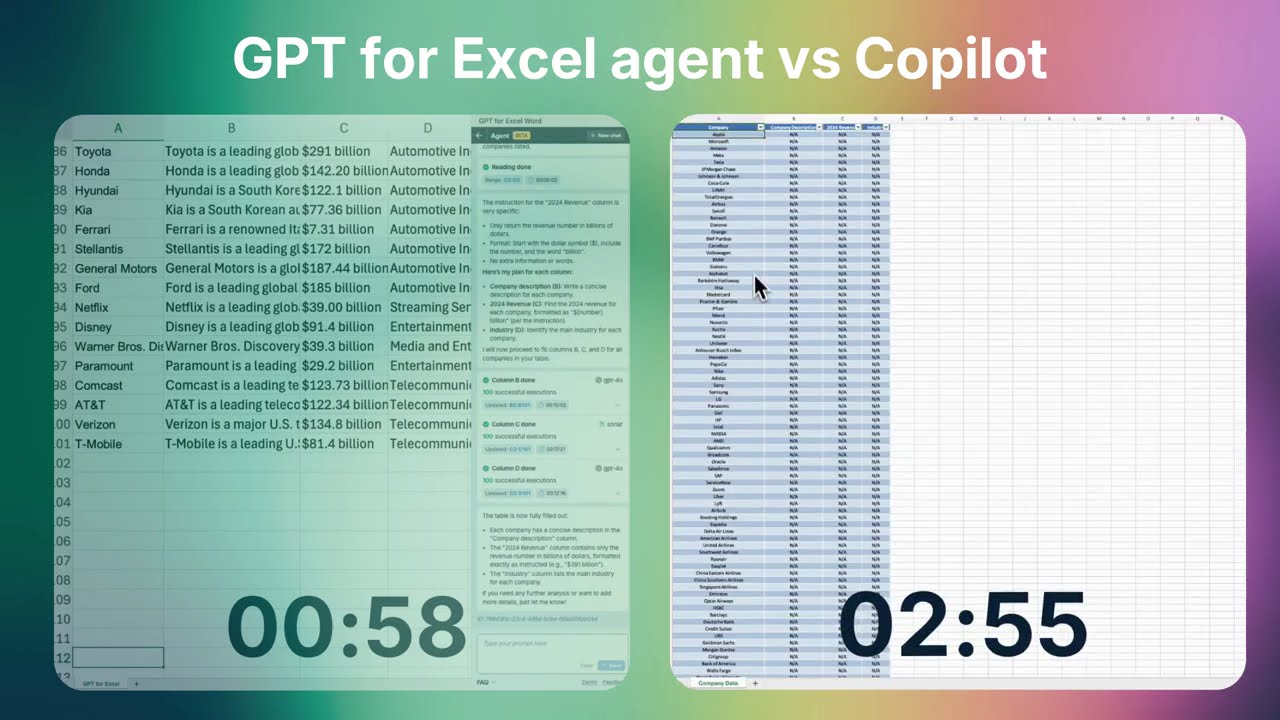
When it comes to executing bulk LLM requests - sending multiple requests to an LLM provider at once - GPT for Excel performs much more reliably than Copilot. This video compares each tool’s agent UI, which follow a ChatGPT-like workflow: users enter a request and the agent produces the corresponding response within the sheet.
When tested on a simple table of web research tasks, GPT for Excel completed the entire workflow from a single prompt: “Fill out this table.” It understood the instruction in the context of the worksheet, performed the necessary web lookups for each row, and inserted the results directly into the appropriate cells autonomously.
In contrast, Copilot was unable to complete the task using its agent UI. It repeatedly created preview tables restricted to an arbitrary number of rows, none of which could be pasted into a spreadsheet in a usable format. When asked to export a .csv file instead, it produced a table filled mostly with “N/A” values. Even after multiple prompts and significant waiting time, Copilot could neither retrieve the correct information nor insert it into the workbook. As a result, in these tests, Copilot was not able to handle bulk workflows reliably. Placed side by side, the difference is clear. GPT for Excel significantly reduced manual effort by performing 300 internet searches in under a minute. Copilot, on the other hand, ended up spending 6 minutes to only produce a .csv file of missing values. For repeated tasks at scale, GPT for Excel proved more capable in testing, whereas Copilot was less consistent with larger workloads.
AI functions comparison: GPT() vs. COPILOT()
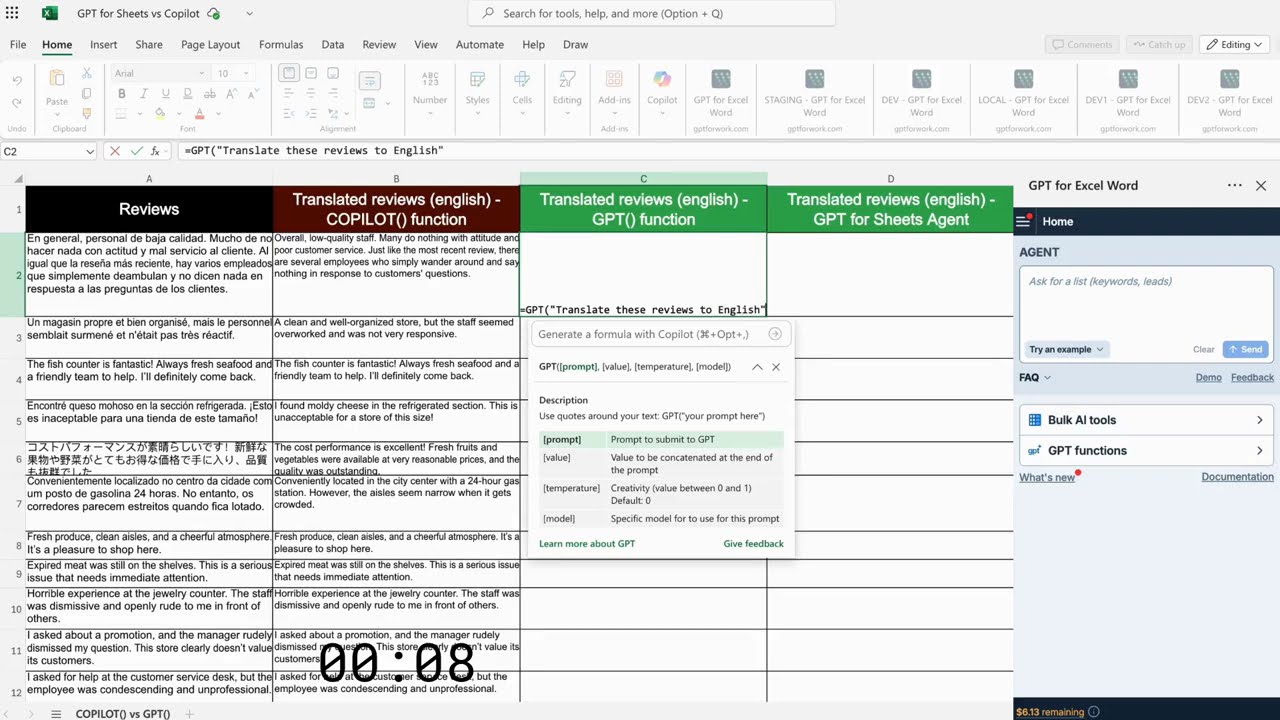
Feature | Model | Speed (rows/second) |
|---|---|---|
🟦 COPILOT() | Undisclosed | 9 |
🟩 GPT() | gpt-4o-mini | 9 |
🟩 GPT for Excel Agent | gpt-4o | 12 |
Although Copilot’s COPILOT() function is intended for bulk operations, it still turns out to be more limited in practice. Because the agent UI cannot deal with bulk tasks, its function-based interface performs somewhat better. With functions, users can enter a prompt into a formula and copy it across rows to request multiple outputs at once.
However, Copilot’s functions are still severely limited when it comes to bulk processing. In this test, both tools were used to translate 1,000 multilingual reviews to English via their functions. Copilot –– after several retries –– was only able to complete 40 translations despite its own documentation stating it can perform 100 function calculations within 10 minutes.
This ceiling makes Copilot’s function calls unsuitable for bulk tasks that exceed roughly 100 cells. Many real-world bulk operations commonly involve hundreds or even thousands of rows, meaning Copilot’s functional approach did not scale to larger workloads in the tests performed. Learn more about Copilot's function limitations on Microsoft's documentation.
By comparison, GPT for Excel handled the task effortlessly. It completed 1,000 translations in just over a minute and can even scale up to one million rows. In the time it takes Copilot to restart small batches every 10 minutes, GPT for Excel can process tens of thousands of rows at once without slowing down. Ultimately, Copilot’s functions can only nibble at bulk processing; GPT for Excel is built for it.
GPT for Excel is extremely fast and reliable at scale
The video demonstrations make it clear that GPT for Excel is consistently faster and more reliable than Copilot. Both of Copilot’s interfaces struggled to complete even simple bulk tasks. Copilot frequently returned unusable preview or N/A-filled tables, while its functions hit its strict limits and were blocked after just a few rows.
Because Copilot’s limits activate quickly on large tasks, it is difficult to generate directly comparable benchmarks. The only concrete limit to be measured is its function ceiling of 100 rows every 10 minutes. Conversely, GPT for Excel can process up to one million rows in a single run at a speed of up to ~36,000 operations per hour. In comparative terms, GPT for Excel is over 100 times faster and can process 999,900 more rows in one run. Therefore, for automation purposes, GPT for Excel is the only tool that delivers both speed and reliability at scale.
Only GPT for Excel can do bulk web research

Bulk internet searches are a major opportunity for automation, as they are extremely laborious to perform manually. However, Copilot does not have live access to the web; it relies entirely on its pretrained model knowledge. In the test in the video, this allows it to answer static factual questions — such as identifying Amazon’s CEO — but prevents it from retrieving current information like its 2024 revenue. Therefore, even if Copilot’s bulk-processing limits were ignored, it still does not support live web lookups, which further restricts its usefulness in automating spreadsheet workflows.
By contrast, GPT for Excel can automate bulk web research as observed in the test demonstration. Through its integrations with Perplexity’s Sonar models and Google’s Gemini with search grounding, it can retrieve both up-to-date and highly niche information from Apple’s 2024 revenue, to specific SKU codes and write the results directly into the spreadsheet. This enables GPT for Excel to replace hours of manual searching with a single prompt, delivering significant time savings for anyone needing to research the web at scale.
Bulk image analysis is exclusive to GPT for Excel
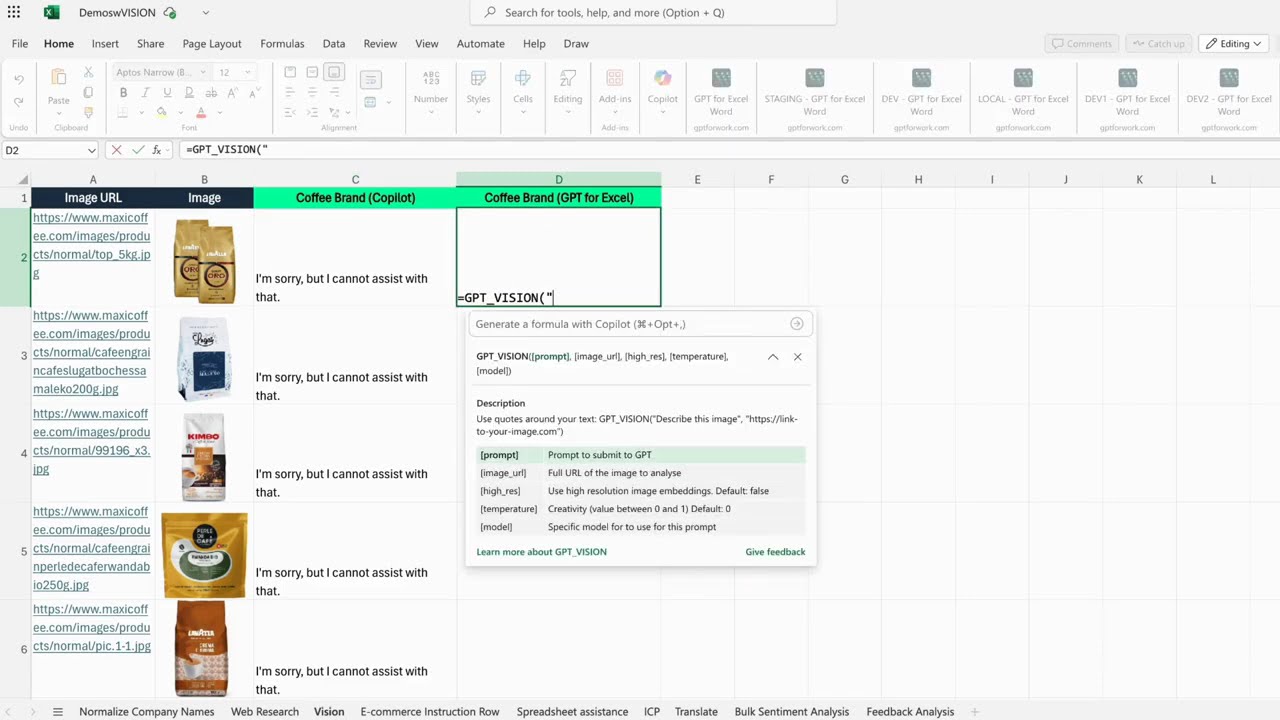
Extracting information from images is another tedious task that can benefit from LLMs’ multimodal analysis. However, Copilot in Excel cannot process images at all. In the video demonstration, it was unable to analyze the product images or identify their brand.
GPT for Excel, on the other hand, handled the task with ease. It quickly extracted the brand name from each image and wrote the results directly into the sheet. High-level tasks like this can now be automated end-to-end with GPT for Excel, saving users significant time when working with image-based data.
Choose your AI provider and models in GPT for Excel
With Copilot, users have no visibility into which model is being used behind the scenes, nor any ability to choose or adjust it. This makes precise prompting more difficult, especially for advanced tasks.
GPT for Excel, by contrast, gives users full control over the underlying model. You can select from leading AI providers and choose between specific model versions such as gpt-5.1, claude-4.5-sonnet, or gemini-2.5-flash depending on what your workflow requires. This flexibility allows users to tailor both performance and cost to the task at hand.
Copilot’s strengths
While GPT for Excel clearly dominates the integration of AI into Excel for bulk processing, Copilot does have its strengths. For instance, it offers several spreadsheet-native capabilities that GPT for Excel does not yet support. It can take a dataset and produce a bar chart, scatter plot, or line graph with labelled axes and a suggested title. It can also rearrange tables into pivot summaries, create grouped views, or apply conditional formatting to highlight trends and outliers. Beyond these visual features, both Copilot and GPT for Excel can analyze data directly through their chatboxes, offering summaries, trend explanations, anomaly detection, and descriptive insights without requiring any formulas or technical knowledge.
Together, these features make Copilot particularly appealing to users who are less familiar with Excel’s interface. A novice user who may not know how to build a pivot table or configure chart settings can ask Copilot to “summarize sales by region” or “visualize monthly trends”, and receive a polished output without navigating multiple menus. However, the time saved is minimal for existing users who are able to do these tasks much quicker than Copilot. Hence, while these features make Copilot a helpful companion for beginners, they still fall far short of the time savings that GPT for Excel delivers for bulk workflows.
Pricing comparison
Another important distinction is the pricing model. Copilot in Excel is bundled with Copilot across all Microsoft 365 applications and costs ~$360 per user per year with heavily rate limited usage. While this gives you broad access across the Office suite, its value depends heavily on how much you actually rely on Copilot inside Excel. If your needs go beyond guided assistance and visual features, much of that subscription cost goes unused.
GPT for Excel is pay-as-you-go. There are no artificial limits on how many operations you can run, and usage scales entirely with your AI provider. You can process thousands of rows in one go, choose the model that best fits your needs, and only pay for what you use. This flexibility ensures that large or occasional high-volume tasks are never blocked by hidden ceilings or subscription constraints.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Copilot in Excel used for?
Copilot in Excel is aimed at guided assistance: summaries, explanations, charts, and simple transformations. It’s helpful for quick insights rather than high-volume automation.
Why does Copilot struggle with large datasets?
Copilot often stops when tasks involve hundreds or thousands of rows. It may output partial previews, stall mid-process, or fall back to downloadable CSVs. Larger workloads are typically handled more reliably by GPT for Excel, which runs full-range operations directly in the sheet.
Can Copilot process full tables directly in Excel?
Not consistently. Copilot frequently inserts only fragments of a table or places results outside the intended range. When users need complete, in-sheet outputs, GPT for Excel provides a more stable workflow.
Does Copilot support bulk processing in Excel?
Copilot’s processing limits make it suitable for smaller tasks, not multi-thousand-row operations. Workbooks that require bulk updates are generally better served with GPT for Excel, which is engineered for high-volume execution.
Can Copilot perform live web searches?
No. Copilot doesn’t have access to live internet data while running inside Excel. When the task depends on current information, users often turn to GPT for Excel, which can run real-time lookups and write results directly inside the workbook.
Does Copilot support image analysis in Excel?
No. Copilot cannot interpret or extract data from images inside Excel. Image-heavy workflows such as reading labels or classifying product photos, are better managed by GPT for Excel, which supports bulk image extraction.
Is Copilot suitable for repetitive or multi-step workflows?
Copilot works well for short, interactive tasks. For large datasets or multi-step automation, GPT for Excel typically handles those workflows more consistently inside the sheet.
How is Copilot priced compared to alternatives?
Copilot is licensed at ~$360 per user per year and covers the full Microsoft 365 suite. For teams that prefer usage-based billing, GPT for Excel operates on a pay-as-you-go model where you only pay for the AI you run.
Conclusion
Copilot and GPT for Excel may share similar interfaces, but the value they offer inside Excel is fundamentally different. Copilot improves accessibility for beginners: it can generate charts, build pivot tables, and explain your data. But when the work goes beyond simple summaries or small datasets, Copilot’s current limitations become more noticeable: preview-only outputs, unusable CSV exports, slow execution, and strict function-call limits. Therefore, Copilot may make Excel easier to approach, but it is not optimized for speeding up heavy workloads.
GPT for Excel, by comparison, excels at heavy workloads. By executing large volumes of LLM operations directly into the spreadsheet, GPT for Excel turns time-consuming, repetitive tasks into a single prompt. Whether it’s translating thousands of reviews, performing wide-scale internet research, or analyzing images in bulk, GPT for Excel consistently completes tasks in seconds that would otherwise take hours. For anyone who relies on Excel to process substantial workloads, GPT for Excel is the tool that fundamentally levels up how quickly and reliably the work gets done.


